Home > About Us > Corporate Social Responsibility > Sustainability Report > Sustainability Report 2006 > Environmentally Friendly Manufacturing (1) Measures against Global Warming
| Environmental Management Sustainability Report 2006 |
|||
| Environmentally Friendly Manufacturing (1) Measures against Global Warming |
Global warming is believed to be caused by the increase of greenhouse gases, such as carbon dioxide and methane, created by human activity. The Kyoto Protocol went into effect in February 2005, and preventive measures are being undertaken at an international level. Kobe Steel and its group companies are implementing energy-saving activities and reviewing energy use in their operations, in accordance with voluntary action plans in their respective industries. |
| Energy Savings in Production Processes |
| At steelworks and plants, efforts have been made to greatly reduce energy consumption. Measures include implementing concatenated processes, introducing large exhaust heat recovery equipment, and minimizing the number of heating and cooling processes. At the same time, we are developing new iron-making technologies for higher energy savings and lower impact on the environment. In 1990 we started switching from oil-based fuel to city gas, which releases far less carbon dioxide. In 2005 gas accounted for 2.7% of the energy used in Kobe Steel Group companies. Kobe Steel's Iron and Steel Sector accounts for 97% of the company's output of CO2. |
Breakdown of Energy Sources and Amount Used (including 45 domestic Group companies)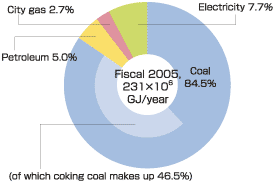 |
| Voluntary Action Program Voluntary Action Program in Industry |
|||||||||||
|
| Iron and Steel Sector | |
At Kakogawa and Kobe Works, concatenated processes in steelmaking, recovering and reusing waste heat from processing, and new energy-saving technology have been implemented since the 1970s. In 2000, a high level of energy savings was achieved by utilizing waste resources effectively such as waste plastic in the blast furnace, updating the facilities, and making use of new technologies. We are also helping to limit global warming by saving energy in other industrial sectors, for example through the development of environmentally friendly products such as high strength steel sheet that is used to make lighter weight automobiles. |
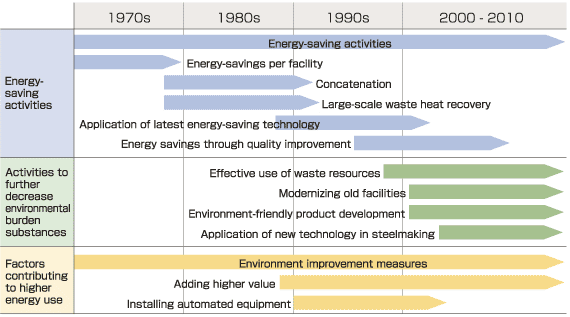
| Although steel production increased in fiscal 2005, additional power generation equipment using recovered blast furnace gas, the increased use of waste plastic, and electricity-saving activities at production facilities contributed to a slight decrease in specific energy consumption and CO2 emissions. Under the current medium-term business plan, Kobe Steel intends to make equipment investments to reduce energy consumption and CO2 emissions. Examples of such projects are increasing waste plastic treatment equipment, refurbishing waste heat recovery equipment, increasing power generation efficiency by improving turbine efficiency, and improving waste heat recovery at the sintering plant, heating furnaces at the rolling mills, and sheet annealing furnace. The Company will continue its switch from oil-based fuel, such as LPG and heavy oil, to city gas. With attention to changes in production volume, Kobe Steel intends to undertake additional energy-saving investments, following the Kyoto Mechanisms, to carry out the steel industry's voluntary action program. |
Changes in CO2 Emissions (estimated value) and Index of CO2 Emissions per Unit (Iron and Steel Sector) 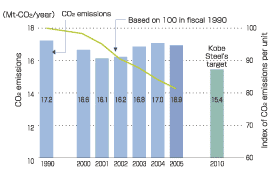 |
Changes in Energy Consumption Index at Kakogawa Works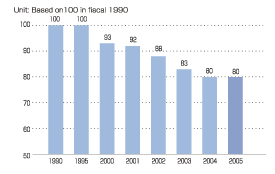 |
| Production Flow and Main Energy Savings |
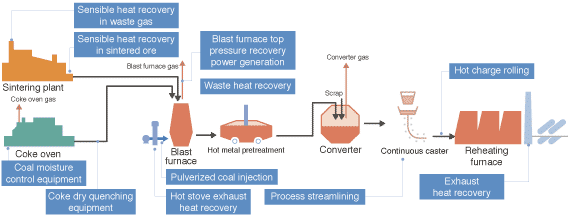 |
| Aluminum and Copper Company | |
| The Aluminum and Copper Company is promoting energy savings in accordance with the voluntary action plan of the Japan Aluminium Association and Japan Copper and Brass Association. At plants and works we are cutting emissions of CO2 by boosting the efficiency of facilities and converting to fuels that release less CO2. For example, at the Chofu Works, since March 2005 we have been switching the fuel base for aluminum melting furnaces from bunker C oil and kerosene to LNG. This is expected to reduce annual CO2 emission by 5%. The Daian Plant is also switching its fuel base from kerosene to natural gas, and expects to reduce the annual CO2 emission rate by 7%. |
Changes in Energy Consumption Rate and CO2 Emission (estimated value)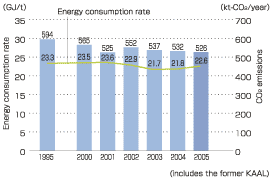 |
| Energy Savings in Logistics |
| Kobe Steel is striving to improve distribution efficiency by unifying administrative and back office operations. Efforts include achieving optimum and quick domestic and overseas raw material distribution as well as optimum and quick product distribution inside the plants and works and from the plants and works to customers. In addition, each office and group company is also making efforts to reduce carbon dioxide emission. Efforts include introducing eco cars and "idling stop" campaigns for all commercial cars in our business operations. |
 One of Japan's largest unloaders is operating at Shinko Kobe Power Station. |
| Iron and Steel Sector | |
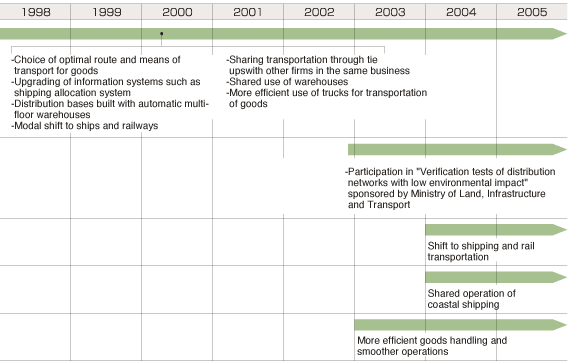
| Efforts have been made to improve the efficient transportation of products by selecting the optimal routes and means of transport and upgrading information systems such as the shipping allocation system. Since 2003, action has been taken to deliver products as close to the customer as possible by ship or rail, cutting the distance traveled by trucks, in a modal shift of transport means. Changes affecting about 20,000 tons of cargo per month in the three years from 2003 to 2005 resulted in a 3% cut in CO2 generated by transportation. As part of a three-way alliance, Kobe Steel cooperates with Nippon Steel Corporation and Sumitomo Metal Industries in transportation. One measure is the joint operation of vessels in domestic waters. Instead of returning empty after delivering cargo, ships now take on cargo from any of the three companies. This improves efficiency and lowers energy consumption. To comply with revised energy saving legislation that came into force in April 2006, we are investigating how much energy is consumed through transportation, and are formulating plans to save energy. Under the medium-term business plan, more focused efforts will be directed to modal shifting and improving the efficiency of transportation by ship and truck. There are plans to replace the current iron ore carriers used between the Kakogawa and Kobe Works, as they age, with larger ships to improve efficiency. Trucks and trailers used for transportation purposes are gradually being replaced with more fuel-efficient vehicles. |
 Loading a container with steel wire rod  Offloading from a trailer |
| Welding Company | |
| The Welding Company's efforts include selecting appropriate modes of transportation in accordance with shipment volume and modal shifting to ships and railways. |
| Aluminum and Copper Company | |
| The Aluminum and Copper Company promotes joint distribution with other companies in the same field. For example, the Moka Plant is increasing transportion efficiency through joint vehicle allocation with Sumitomo Light Metal Industries, Ltd. The Chofu Works is also expanding its energy-saving measures such as joint truck delivery and joint utilization of warehouses. Also, the Moka Plant changed the landing port for some of its imported aluminum ingots from Yokohama Port to Hitachinaka Port, which is closer to Moka, reducing the transportation distance in half. When using Yokohama Port, efforts are made to improve transportation efficiency by taking on exports as cargo on the return trip. As a result, the energy used in the domestic distribution of imported ingots is reduced by 7%. Since 2005, we have also been promoting a modal shift to railways and ferries. |
| Group Company Activities Undertaken to Reduce Global Warming |
|
| ECOWAY Office Activities |
| Under the Kobe Steel Group's Ecoway Office Activities, air conditioning is set at 28 degrees C (82 F) in the summer and 20 degrees C (68 F) in the winter at the head offices, branch offices and sales offices. In the summer, employees are no longer required to wear neckties. Other activities include turning off lights during lunchtime, using energy-saving lighting, and using energy-saving computers. |
|




