Home > About Us > Corporate Social Responsibility > Sustainability Report > Environmental Sustainability Report 2004
| Environmental Management Environmental Sustainability Report 2004 |
|||
| Environment-friendly Production (1) |
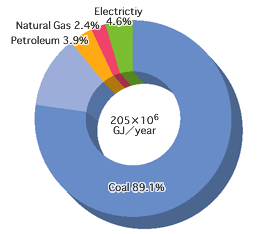
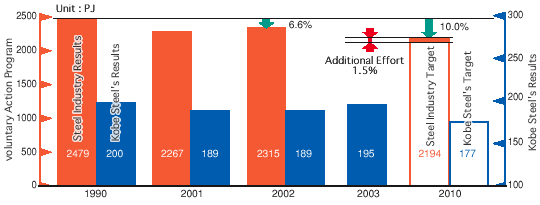
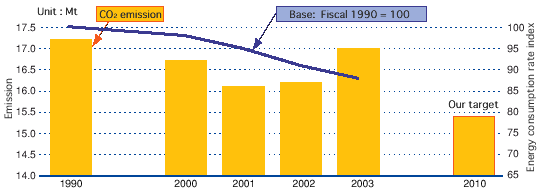
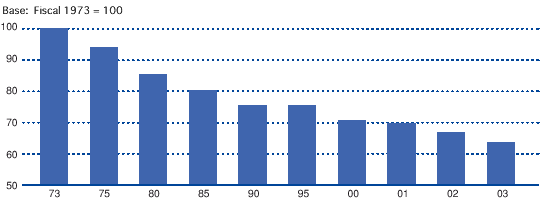
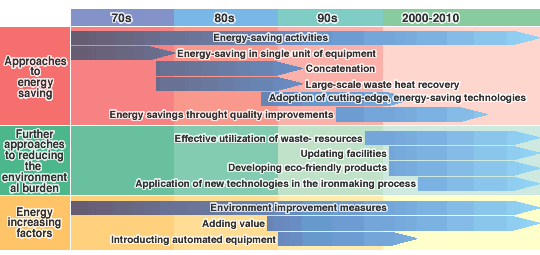
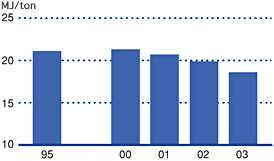
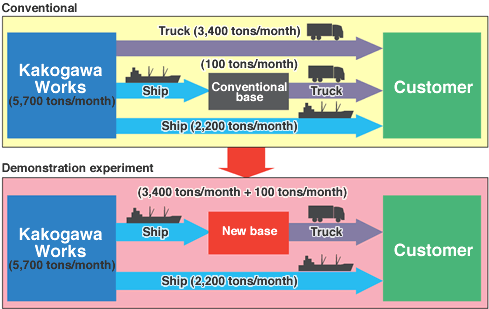
 Global warming is believed to be caused by the increase of greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide and methane emitted through the massive use of fossil fuels. At an international level, preventive measures are being undertaken. Kobe Steel and its group companies are implementing energy-saving activities and reviewing energy use in their operations, in accordance with voluntary action plans in the respective industries. 
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||