Home > About Us > Corporate Social Responsibility > Sustainability Report > Environmental Sustainability Report 2004
| Environmental Management Environmental Sustainability Report 2004 |
|||
| Environment-friendly Production (2) |
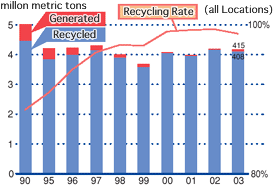
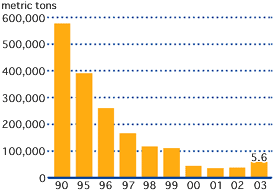
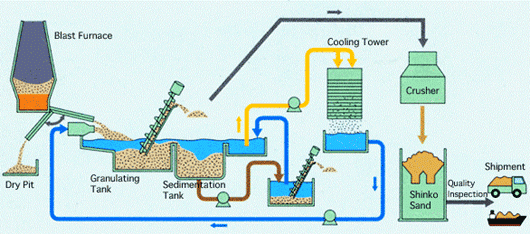
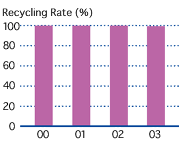
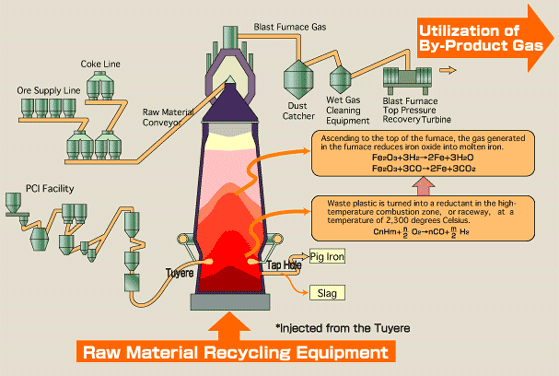
 To build a recycling-based society, the first priority is to reduce generation of waste as much as possible. For waste whose generation cannot be prevented, it is important to recycle the waste to whatever degree possible. Kobe Steelis actively participating in the building of a recycling-based society. At works and plants, efforts are being made to reduce waste by increasing product yield and using waste plastic generated by society.
Activities at Other Group Companies
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||