Home > About Us > Corporate Social Responsibility > Sustainability Report > Sustainability Report 2006 > Contribution to Environmental Protection through Products, Technologies and Services (5) New Energy
| Environmental Management Sustainability Report 2006 |
|||
| Contribution to Environmental Protection through Products, Technologies and Services (5) |
| New Energy and Waste Heat Utilization |
| Small Hydroelectric Generator Operates on as Little as 2 Liters of Water Per Second | |
| Shinko Electric Co., Ltd. has developed a small hydroelectric generator that can produce electricity with a water flow as low as 2 liters per second. Two models are available: one with a 0.5 kW generating capacity (weighing 50 kg) and the other with a 1 kW generating capacity (weighing 75 kg). Because both of these ultra-compact units can generate electricity using only a few liters of water per second, they can be installed just about anywhere there is flowing water, including small mountain streams or factory wastewater outlets. Only a small installation space is needed, and there is no danger that the unit will contaminate the water that passes through. Fast and easy setup can be completed in half a day, requiring the simple connection of hoses to the intake and outlet ports. The intake port is specially designed to prevent clogging by fallen leaves and other debris. With the implementation of the Kyoto Protocol and skyrocketing oil prices, demand is rising for alternative forms of energy. This generator is especially well suited for residential and small office applications. |
 Compact hydroelectric power generator |
| Heat Energy Transport Technology Developed | |
| Kobe Steel, Ltd. and Kobelco Eco-Solutions Co., Ltd. have developed technology that can store low- to medium-temperature heat energy (below 200°C) in a thermal storage unit, which can then be transported to remote areas via truck. Currently, steelworks, factories, waste incineration plants and other facilities simply release low- to medium-temperature waste heat without attempting to reuse it. A proprietary technology developed by these two companies uses erythritol (which has a melting point of 119°C) as the thermal storage material. In transport tests, hot water was successfully maintained at 90°C, a world first. Applications go beyond hot water supply to include energy for cooling systems. No pipelines or other infrastructure are needed, making this a highly effective heat energy source that helps to reduce CO2 gas emissions and combat global warming. |
 Truck carrying a thermal storage unit |
| Hydrogen energy utilization: High-purity hydrogen and oxygen generation system | |
| Kobelco Eco-Solutions Co., Ltd. developed a landmark device, a high-purity hydrogen and oxygen generation system called HHOG. It uses a proton exchange membrane to generate high-purity hydrogen and oxygen from pure water. Hydrogen is noted as a next-generation energy alternative to fossil fuels. HHOG can generate hydrogen from only electricity and water. Also, it does not emit such gasses as CO2 that cause global warming. Owing to these features, sales of the equipment are steadily increasing in and outside Japan. HHOG is installed at hydrogen refueling stations for fuel cell vehicles in Yakushima, Kyushu, Japan, which is registered on the World Heritage list. Also, Kobe Steel has developed the world's first 1,000 bar (100 MPa) ultra-high pressure compressor for hydrogen refueling stations that supply hydrogen gas to fuel cell vehicles. The system combines an oil-free piston compressor with a diaphragm head, combining ultra-high pressure and large capacity in one compact compressor unit.
|
Mechanism of hydrogen gas generation A proton exchange membrane acts as the electrolyte. Electrocatalysts are bonded on both sides of the membrane. Deionized water fed into the anode chamber is decomposed into oxygen and the ion H+. The ion passes through the membrane to the cathode by force of the electrical field. The ion obtains electrons and generates hydrogen gas. 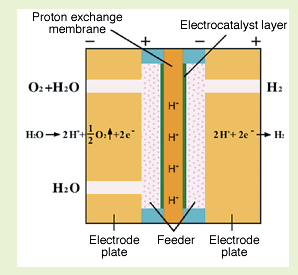 |
|
|||||
| Soyokaze-kun Compact Wind Power Generation Systems | |
| Shinko Electric Co., Ltd. has applied cutting edge technologies in the fields of aircraft engineering, clutches, AC generators and controllers to develop the Soyokaze-kun series of small, wind power generation systems. Unlike conventional propeller type generators, this series features a unique vertical-shaft windmill made of aluminum sheet from Kobe Steel, which can very efficiently generate electricity with a wind speed of just 2 meters per second, regardless of wind direction. The use of solar panels results in hybrid power generating capacity (wind + solar) with an AC100V output that can be used by virtually any household appliance in Japan. The unit operates quietly, making it suitable for residential areas. It is used in general households and small offices, on street lamps, in shops, on farms and isolated islands, and also as an auxiliary power supply for communication systems in times of disaster. As many as four vertical-shaft windmills can be stacked on top of each other to create a high power unit with a 10 kW capacity. The use of a solar panel installed at the top of the windmill tower further promotes the utilization of renewable energy resources. Requiring a space of just 4 m x 4 m and between 12 m and 14 m of open height, this stacked version of Soyokaze-kun is extremely compact and easy to install. The first commercial order was received from Kosai, Shizuoka Prefecture as a power source for a hot footbath at the highway rest stop Michi no Eki Shiomizaka. |
 Tandem-type wind power generation system |





