Home > About Us > Corporate Social Responsibility > Sustainability Report > Sustainability Report 2007 > 1. Environmentally Friendly Manufacturing (4)
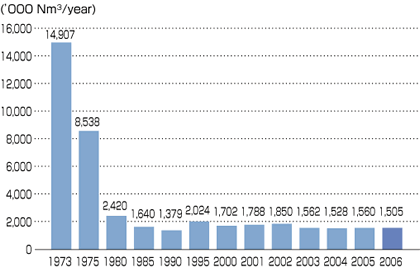
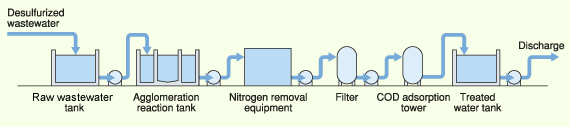
Lowering Environmental Impact (Air, Water, Noise, Odors, Soil)
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Home > About Us > Corporate Social Responsibility > Sustainability Report > Sustainability Report 2007 > 1. Environmentally Friendly Manufacturing (4)
Lowering Environmental Impact (Air, Water, Noise, Odors, Soil)


|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||