Home > About Us > Sustainability Management > Sustainability Report > Sustainability Report 2011 > Measures Against Global Warming
 Measures Against Global Warming
Measures Against Global Warming
| Saving energy in every aspect of our business activities, developing energy saving technology, and reducing greenhouse emissions |
Now more than ever, companies need to take action to urgently address the issue of global warming.
The Kobe Steel Group is tackling this issue by moving forward on R&D and rationalizing energy use through energy conservation, among other steps taken across its various business activities. The Group is working to achieve the goals of each industry's voluntary action plans as well as to further conserve energy and reduce CO2 emissions.
Energy Conservation in Production Processes
In fiscal 2010, the Kobe Steel Group as a whole consumed 223 PJ (petajoules) of energy. Our Iron & Steel Business accounted for approximately 95% of this total, with our Aluminum & Copper Business accounting for a further 4%.
We continue to implement energy saving measures, including the installation of high-efficiency equipment and recovering exhaust heat. We are also taking steps to improve operational processes, in areas such as combustion management and production efficiency, across all of our lines of business.
Energy Use by Segment (including group companies)
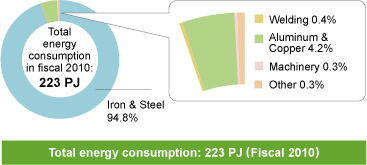
Iron & Steel Business
The Iron & Steel Business has been working to save energy ever since the two oil crises in the 1970s, through measures such as continuous processes, exhaust heat recovery and injecting pulverized coal into our blast furnaces. Since the latter half of the 1990s, we have been working to save energy and reduce CO2 emissions in an effort to achieve voluntary action plan targets for greenhouse gas emissions set forth by Japan’s steel industry.
As a result, we have nearly finished installing all major energy saving equipment that has reached the commercial stage of development. We are nonetheless continuing to implement energy saving measures, through initiatives such as further increasing the efficiency of our facilities and improving operational processes.
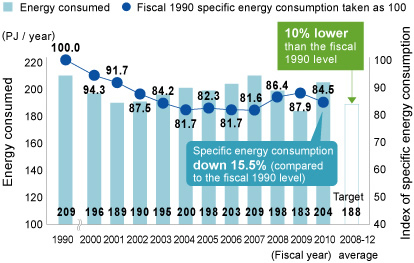
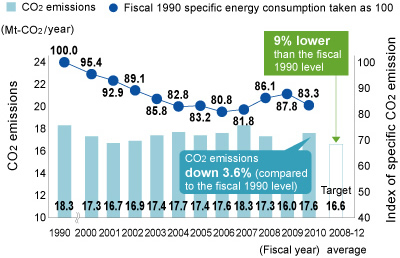
Measures implemented during fiscal 2010 included increasing compressor efficiency and reducing pressure and loss from continuous spray caster nozzles (Kakogawa), fitting inverters to electric motors to improve operations (Kobe), and upgrading reheating furnaces and reviewing boiler operations (Takasago). We have also got high efficiency gas turbines up and running at our Kakogawa Works, and expect them to make a significant difference in reducing CO2 emissions in the future. As a result, we have improved specific energy consumption per metric ton of crude steel by 15.5% compared to fiscal 1990. In spite of a 16% increase from fiscal 1990 in crude steel production, we have managed to reduce CO2 emissions by 3.6%.
In addition to continuing with energy saving measures in the future, we are also planning to explore the Kyoto mechanisms as a means of dealing with changes in CO2 emissions due to varying production, to enable us to achieve our voluntary action plan targets.
Trends in Energy Consumption and Specific Energy Consumption (approximate figures)
Trends in CO2 Emissions and Specific CO2 Emissions Index (approximate figures)
Notes: Aggregate figures for the Iron & Steel Business, including coke production.
Approximate figures based on Comprehensive Energy Statistics (calorific values) and National Greenhouse Gas Inventories (emission coefficients)
Fiscal 2009 emission coefficient used for fiscal 2010 due to nondisclosure of fiscal 2010 coefficient for purchased electricity
Welding Business
We continue to achieve substantial reductions in CO2 emissions as part of our Welding Business, thanks to measures aimed at integrating production, saving energy and improving efficiency.
Although CO2 emissions were up during fiscal 2010, due to a year-on-year increase in production, we nonetheless managed to significantly improve specific energy consumption through energy saving measures such as fitting inverters to electric motors, reducing air leaks and stabilizing operating patterns, and through improvements such as replacing and increasing the efficiency of air conditioning systems and air compressors.
Trends in CO2 Emissions and Specific CO2 Emissions Index (approximate figures)
Aluminum & Copper Business
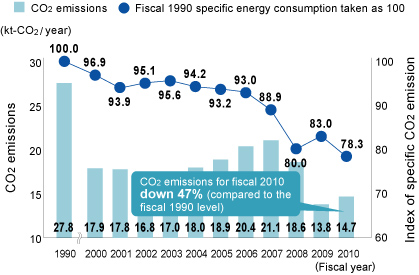
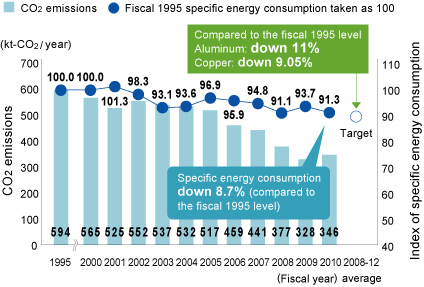
We are continuing to gradually switch fuels from oil-based fuels to natural gas in our Aluminum & Copper Business. At the same time, we are working to consolidate our facilities and improve efficiency. In fiscal 2010, we managed to improve specific energy consumption by 2.6% year on year through energy saving measures such as optimizing operations (fitting inverters to electric motors, etc.) and reducing loss from steam systems, and by restoring production levels. CO2 emissions were down by 42% compared to fiscal 1995 (base year) as a result of our efforts to consolidate production.
Trends in CO2 Emissions and Specific Energy Consumption (approximate figures)
Machinery Business
With growing demand for products such as energy-saving compressors, heat pumps and oil refining pressure vessels, we have continued to improve energy efficiency in the Machinery Business through energy saving measures, improved production efficiency and increased productivity.
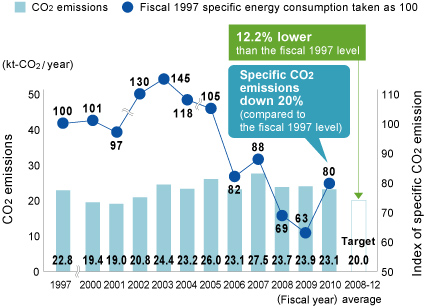
In fiscal 2010, we managed to cut CO2 emissions by 3.3% compared to the previous year, through initiatives such as upgrading air conditioning systems and installing energy saving lighting. Lower production was also a factor. Although specific CO2 emissions per unit of production increased year-on-year, they were still down 20% compared to fiscal 1997, the base year.
Trends in CO2 Emissions and Specific CO2 Emissions Index (approximate figures)
Topics
High-efficiency Gas Turbine Up and Running at the Kakogawa Works|
We are installing a new in-house power generation system at our Kakogawa Works, powered primarily by gas produced by the Works’ blast furnaces. As we were upgrading our generation equipment for the first time in over 30 years, we took the opportunity to install a high-efficiency gas turbine, which is fully up and running now that construction has been completed. By improving power generation efficiency, saving on auxiliary fuel and reducing the amount of electricity purchased, we are projecting that we will be able to reduce CO2 emissions by approximately 100,000 metric tons a year. |
 |
Energy Savings in Logistics
At the Kobe Steel Group, we are committed to conserving energy through optimum logistics at every stage of our activities, from shipping in raw materials from all over the world and transporting materials in-house, to delivering products to our customers.
We are currently promoting a modal shift in each of our businesses, in an effort to transport more products via rail or sea rather than by road. We are also taking steps to improve efficiency during shipping, including increasing load efficiency and using larger vehicles.
In our Iron & Steel Business, we ship a high percentage of products by sea. We have improved efficiency by introducing larger carriers and reducing ship turnaround and cargo handling times. We have also achieved significant results through initiatives such as running joint operations in domestic waters in order to carry combined loads to distant locations, in conjunction with Nippon Steel Corporation and Sumitomo Metal Industries, Ltd., and increasing loads on return journeys.

Combined shipping by road and rail using JR open-top containers

The Shinkomaru iron ore carrier transports cargo from the Kakogawa Works to the Kobe Works
Energy-saving Initiatives at Group Companies
|


