Home > About Us > Sustainability Management > Sustainability Report > Sustainability Report 2014 > Appropriate Management of Chemical Substances
 Appropriate Management of Chemical Substances
Appropriate Management of Chemical Substances
The Kobe Steel Group carries out thorough and appropriate management of chemical substances, in line with domestic and international standards, and endeavors to reduce the use of hazardous substances and replace such substances with safer alternatives.
Thorough Chemical Substance Management
![]()
Kobe Steel has established the Kobe Steel Group Policy on Controlling Hazardous Chemical Substances and pursues thorough chemical substance management.
The use and management of each substance is clarified through Designated Chemical Substance Management Sheets. In addition to tallying transfer and output of substances as required by the PRTR Law*1, we also engage in initiatives to limit the use and output of such substances.
According to reported figures collected under the PRTR Law for each location in the Kobe Steel Group, the Kobe Steel Group handled 51 substances, with a total output*2 of approximately 708 tons, and total transfer*3 of 507 tons.
Kobe Steel Group Output/Transfer of Substances
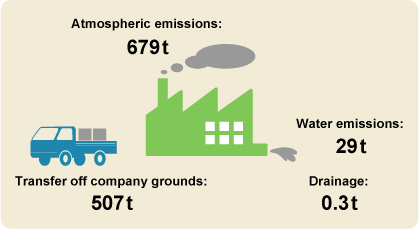
- 1 The Pollutant Release and Transfer Register Law.
- 2 Output includes atmospheric and water emissions.
- 3 Transfer includes transfers of substances off of company grounds and drainage.
Complying with Chemical Substance Regulations
![]()
Both within and outside Japan, worldwide regulations on chemical substances are growing stronger. The Kobe Steel Group complies in an appropriate manner with these laws and regulations.
As shown by the table below, the Group continues to work towards reducing chemical substance output. In order to ensure compliance with relevant laws and regulations, we also share information and opinions between departments.
Management of Waste Electronic Goods Containing PCB
![]()
Transformers, condensers and other used goods containing PCB (polychlorinated biphenyl) are handled at a special depository, as prescribed under the PCB Special Measures Law, with contracted disposal and proper reporting.
Kobe Steel began contracted disposal in fiscal 2008, and continued that practice in fiscal 2013.
In fiscal 2013, it was discovered that the Kakogawa Works had mistakenly shipped insulating oils containing trace amounts of PCB as well as transformers stained with this oil as non-PCB items. In order to avoid reoccurrence of such an incident we carefully revised our rules for management and confirmation of waste, such as those for on-site supervision and observation. We also carried out stringent new training for relevant employees.
To prevent reoccurrence, other Group companies and locations were also informed.
Examples of Activities to Reduce Chemical Substance Releases
![]()
| Company name | Location | Examples of initiatives |
|---|---|---|
| Saijo Plant | Higashihiroshima, Hiroshima Prefecture | Switched from oil-based floor paint to water-based |
| Kobe Corporate Research Laboratories | Kobe, Hyogo Prefecture | Installed active carbon absorption flue gas treatment devices for test equipment that uses large amounts of organic solvents |
| Shinko Kenzai, Ltd. | Amagasaki, Hyogo Prefecture | Switched from paint containing cobalt to non-cobalt paint |
| Nippon Koshuha Steel Co., Ltd. | Imizu, Toyama Prefecture | Switched from dichloromethane for cleaning vacuum pump parts to a non-PRTR cleaning agent Switched from products paints containing organic solvents to water-soluble paints Switched from organic solvent polishing fluid for automatic polishers to non-organic solvent type |
| Shinko Leadmikk Co., Ltd. | Kitakyushu, Fukuoka Prefecture | Extended usage life of stripping solution (through electrolytic removal of impurities) Reduced consumption of hydrocarbon cleaning agents through distillation and reuse |
| Japan Superconductor Technology, Inc. | Kitakyushu, Fukuoka Prefecture | Reduced evaporation of dichloromethane cleaning agents through increased cooling and air-tightness for cleaning tanks |


