The manufacturing sites of the Kobelco Group use large quantities of water for cooling, cleaning, and other purposes, and we recognize that water shortages constitute a risk. There is also the risk of operations being impacted by flood damage such as torrential rain, which tends toward increasing severity. Furthermore, we recognize that violations of environmental laws and regulations, ordinances, and agreements carry the risk of affecting the environment and living things in public waters. On the other hand, we see the business of purifying water and providing safe water as an opportunity.
The WRI Aqueduct evaluation shows that the risk of water shortages and flood damage at our Group domestic production sites is low. Nevertheless, to prepare for all eventualities, we are working to reduce the amount of water resources used and increase the water recycling rate by promoting more efficient water use in the production process and more extensive use of recycled water. In addition, to address wastewater risks, we will not only comply with regulations, but will also strive to reduce the discharge of pollutants into public water areas by cleaning up wastewater from the production process with a treatment system suitable for the characteristics of the wastewater.
The Environmental Management and Disaster Prevention Subcommittee deliberates, reports, and evaluates policies, action plans, and results of initiatives concerning the appropriate management of our Group’s water resources at least once a year. This management cycle is properly implemented. Important matters are reported and submitted to the Executive Council through the Sustainability Management Committee (chair: Executive Vice President and Representative Director), to which the subcommittee reports.
We have set the following targets and are working to address water shortage and wastewater risks
* Hyogo Prefecture has formulated a “Nutrient Management Plan” with the aim of revitalizing the Seto Inland Sea as a “rich and beautiful satoumi, an environment which human interaction and coexistence with the coastal sea increase biological productivity and biodiversity.” In response to the selection of the Kakogawa Works as a “nutrient increase action implementer (nitrogen)” in this plan, the nitrogen emission target stated last year has been removed.
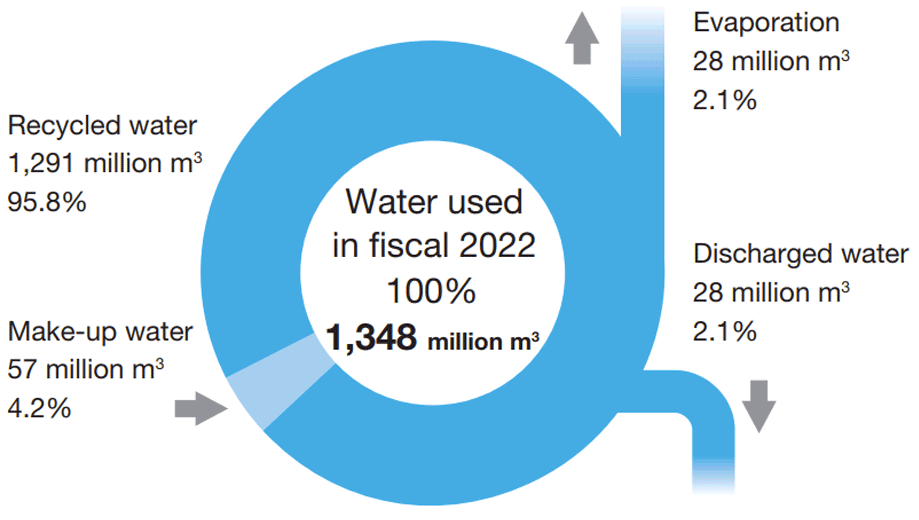
At each business location, we are recycling water to use again at the site after purifying wastewater from each production process through coagulation sedimentation, sand filtering, and other means. Additionally, by purifying water with a treatment system suitable for wastewater from the manufacturing process, we are working to promote the use of recycled water and reduce the pollutant load of wastewater discharged into public water areas.
In the treatment of wastewater, approximately 50% of the total amount is treated with advanced tertiary treatment, reducing the impact of pollution it may cause.
In fiscal 2022, the water recycling rate was 96%, thus achieving the target.
Water pollutant load in fiscal 2022 was COD: 213 tons/year; and total phosphorus: 4 tons/year, thus achieving targets.
Water Intake, Discharge, and Recycling Rate Data for the Past Three Years
(Kobe Steel, Ltd.; Unit: 10,000 m3)1
| Item | Fiscal 2020 | Fiscal 2021 | Fiscal 2022 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Water withdrawal by source | ||||
| Freshwater (tap water and industrial water provided by the waterworks bureau in each area)2 |
4,782 | 5,067 | 5,106 | |
| Groundwater | 510 | 525 | 550 | |
| Seawater for cooling | 257,072 | 263,576 | 337,340 | |
| Water withdrawal total3 | 262,364 | 269,169 | 342,996 | |
| Water discharge total by discharge destination | ||||
| Rivers | 183 | 190 | 201 | |
| Sea water | 259,652 | 266,145 | 339,894 | |
| Sewage | 56 | 71 | 67 | |
| Discharge total | 259,891 | 266,406 | 340,162 | |
| Discharge by each treatment method4 | ||||
| No treatment (including discharge to sewage) | 471 | 426 | 440 | |
| Simple treatment | 900 | 902 | 867 | |
| Standard treatment | 17 | 21 | 20 | |
| Advanced treatment | 1,433 | 1,481 | 1,493 | |
| Freshwater withdrawal and discharge | ||||
| Water withdrawal total | 4,782 | 5,067 | 5,106 | |
| Water discharge total | 2,820 | 2,829 | 2,822 | |
| Consumption | 2,472 | 2,763 | 2,834 | |
| Total recycled water | 124,441 | 125,392 | 129,129 | |
| Recycling rate5 | 96% | 96% | 96% | |
1: Aggregates the boundary of 100% of Kobe Steel’s production sites. It also includes domestic Group companies of a certain scale or larger (water use of 1,000 thousand m3 /year or more). The amount of wastewater at the target business sites covers more than 99% of the entire Group (Japan).
2:The water withdrawal sources for tap water and industrial water are mainly rivers
3:The sum of the breakdown figures and the total might not match due to rounding of each item.
4:Simple treatment: Removing pollutant and floating particle by physical process (e.g., precipitation)
Standard treatment: Decomposes organic matter by biologic treatment
Advanced treatment: Treat suspended particle, colloid and dissolved matter (nutrient, heavy metal, inorganic pollutant, and other pollutant after simple and standard treatment
5:The recycling rate is calculated as: (Total recycled freshwater) / (Total recycled freshwater + Total freshwater withdrawal). The calculation of total recycled freshwater includes some estimates based on equipment specifications.
Data on Water Pollution Load*
| Item | Target | Fiscal 2020 | Fiscal 2021 | Fiscal 2022 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Water discharge total | - | 2,598.13 million m3 | 2,664.06 million m3 | 3,401.62 million m3 |
| COD | 474t | 243t | 244t | 213t |
| Phosphorus | 23t | 3t | 3t | 4t |
* All 10 business sites in areas with risks related to total volume regulations are aggregated, and their wastewater accounts for more than 99% of the Group’s total (Japan).
Each Kobelco Group business site remains aware of regulatory water quality requirements and evaluates their compliance with these levels. Please see below for water discharge data for each business site, including the results of water quality measurements.
Of the Group’s 32 major production sites in Japan, 17 that account for 53% have formulated water management plans, monitor water intake, discharge, and recycling; and are working to properly manage water resources and reduce environmental impact.
At Kakogawa Works, we are promoting the effective use of water resources, such as by monitoring withdrawal and discharge through continuous measurement of flow rates at drains, and by recycling water to use again at the site after purifying wastewater from each production process through coagulation sedimentation, sand filtering, etc. In this way, the water recycling rate reaches approximately 97%.
In Toyama Prefecture, where Nippon Koshuha Steel Co., Ltd. is located, the amount of water allocated to companies is ensured, but in order to leave enough water for snow clearing, every year the prefecture calls on factories, workplaces, offices, and snow-clearing equipment managers to voluntarily save water from December to February. In order to do its part, Nippon Koshuha Steel is working to reduce its water usage as much as possible.
While water quality has improved in the Seto Inland Sea (Harima Sea) due to wastewater regulations, the discoloration of seaweed and the decrease in fish catch due to lack of nutrients have become serious issues.
In response to this situation, the Act on Special Measures concerning Conservation of the Environment of the Seto Inland Sea was revised, and in 2022, Hyogo Prefecture formulated its “Nutrient Management Plan.” Kakogawa Works has been selected as a “nutrient increase action implementer (nitrogen),” and will contribute to the creation of a vibrant ocean by operating in accordance with the Nutrient Management Plan.
As the type and severity of a natural disaster can vary by site, each site regularly checks the latest hazard maps provided by local authorities and prepares for the risk accordingly
Every year, each business site estimates the amount of water it expects to use in the subsequent fiscal year and determines whether the amount of contracted industrial water meets its needs. When a water shortage is anticipated, each business site secures substitute water resources and evaluates how this will affect production.
The Head Office evaluates water stress of the region where the business sites are located with WRI Aqueduct and reports any problems (if any) to necessary directors and officers.
In the WRI Aqueduct assessment for fiscal 2022, none of the Group’s business sites or Group companies in Japan are located in regions of high water stress or above and no production sites posed issues. In addition, we have secured a certain volume of water from the supply sources, and we believe that the risk of water withdrawal affecting production is low.
At Kakogawa Works, for example, the risk of water intake affecting production is thought to be low because upstream from the water used is the Gongen Dam (total storage capacity: 11.12 million m3), constructed to ensure a stable supply of industrial water from the Kakogawa River as well as the Kakogawa Weir (total storage capacity: 1.96 million m3) and Heiso Dam (total storage capacity: 9.40 million m3), which were constructed to ensure the flow rate of industrial water.
As well as identifying risks from past cases of flood damage in areas from which we procure raw materials, we analyze water risk in those areas using WRI Aqueduct, and are working to diversify raw materials suppliers based on the results of this risk analysis.
R&D expenses for water treatment-related projects and water pollution prevention projects used for the prevention of abnormal water discharge or inspection/maintenance of water treatment facilities are presented below.
(Millions of yen)
| Item | Fiscal 2020 | Fiscal 2021 | Fiscal 2022 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Capital investment |
Expense | Capital investment |
Expense | Capital investment |
Expense | |
| Expenses for water pollution prevention* |
210 | 3,940 | 80 | 4,660 | 150 | 5,490 |
| R&D expenses for water treatment-related projects | - | 530 | - | 320 | - | 470 |
* Results for Kobe Steel, Ltd. For details, see the “Environmental Management” page.
We comply with regulatory limits stipulated by laws and regulations. If stricter regulatory limits have been set by agreements with local governments, we strive to comply with them.
There was one case in Japan where water quality values exceeded regulation standards. The case was discovered by self-inspections and promptly reported to the relevant authorities, with action taken. No fines or punishments were imposed.
Overseas Group companies were fined 30,000 yuan (approximately 900,000 yen) for exceeding water quality regulations.
Kobe Steel, Ltd. has been responding to questionnaires from CDP* since fiscal 2009. Please refer to the following for our response to the 2023 Water Security Questionnaire.
* An international NGO working on environmental issues. It sends environment-related questionnaires to companies and compiles the results to analyze and evaluate on a common scale.