December 17, 2020
Kobe Steel, Ltd.
Kobe Steel, Ltd. announces that it will conduct joint research with Mitsui O.S.K. Lines, Ltd. on a binary cycle power generation system*1) currently under development. The binary cycle power generation system has been installed on a bulk carrier (215,000 metric tons, built by Imabari Shipbuilding Co., Ltd. in October 2020) owned by Shunzan Kaiun Co., Ltd.
The two companies will conduct joint research on the ship over the next three years to verify the durability and performance of the equipment under real operating conditions.
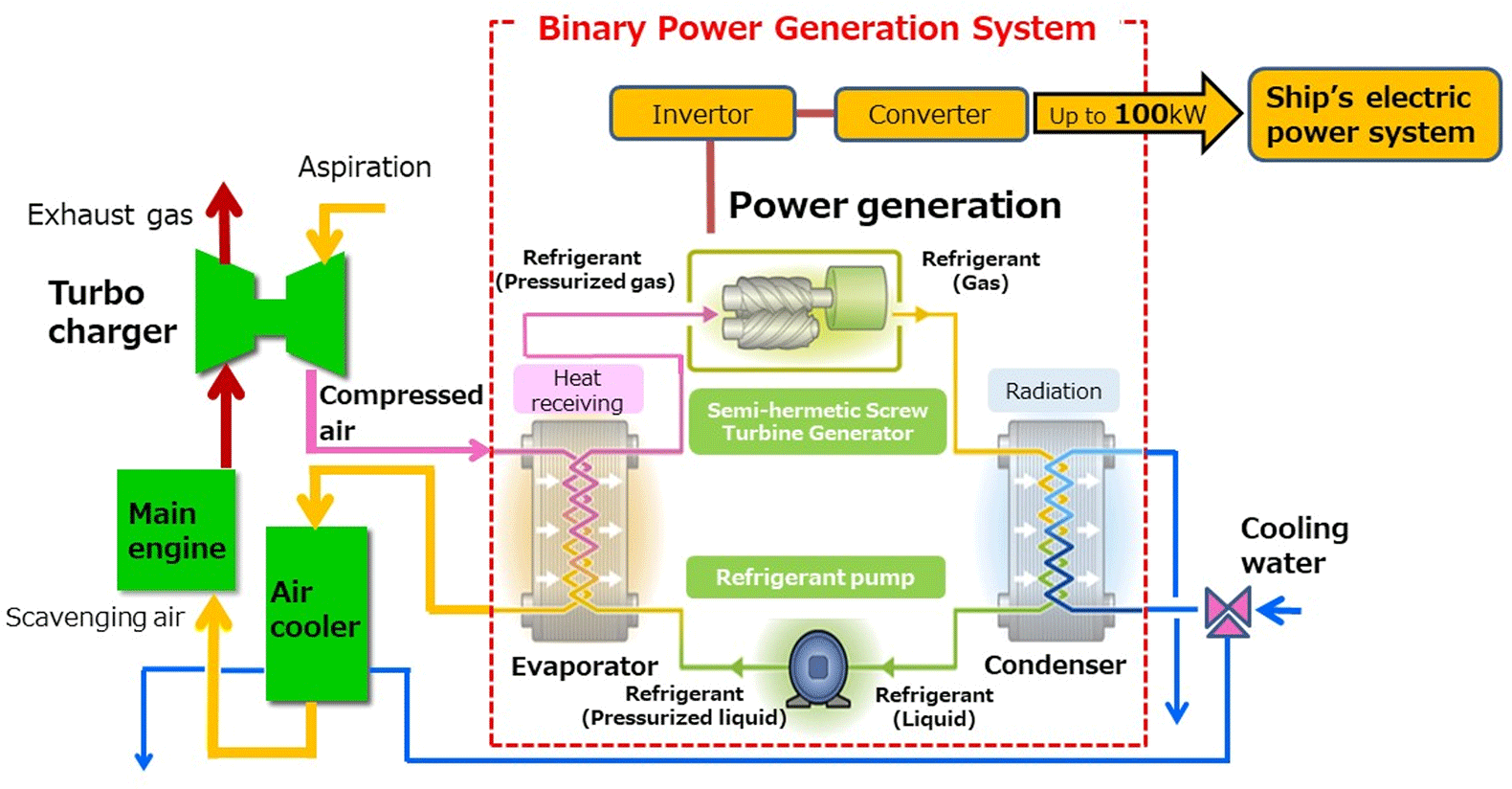
The binary cycle power generation system, installed on a capesize*2) carrier for the first time, can produce electricity up to 100 kW from the waste heat generated in the cooling process of the scavenging air from a turbocharger of the main engine of a ship. Usually, a large part of the generated heat is discarded. By effectively utilizing the waste heat to generate electricity that serves as auxiliary power for the ship, the system contributes to reducing CO2 emissions and fuel for the generator engines.
The shipping industry is urgently pursuing efforts to reduce CO2 emissions by 40 percent by 2030 and 70 percent by 2050 compared with 2008 under a strategy adopted by the International Maritime Organization (IMO)*3).
In 2011, Kobe Steel developed a binary cycle power generation system called Microbinary and began marketing for use on land. Kobe Steel has delivered this equipment to many customers that utilize heat sources such as factory waste heat and terrestrial heat. Based on its knowledge and experience, Kobe Steel began developing a binary cycle power generation system for ships in 2014 focusing on the waste heat from ships. In 2016, Kobe Steel completed sea trials*4) of a prototype and is working to commercialize the system in the future.
The binary cycle power generation system has received basic approval from Japan's ship classification society Nippon Kaiji Kyokai (also known as ClassNK), UK’s Lloyd's Register of Shipping, Norway’s DNV GL, and the American Bureau of Shipping (ABS).
Recognizing CO2 reduction as one of the top management priorities, the Kobe Steel Group (also known as the KOBELCO Group) aims to expand its binary technology globally while contributing to reducing the environmental burden of the shipping industry.
*1) Binary cycle power generation produces electricity with a turbine driven by steam generated by heating and vaporizing a working medium with a low boiling point using a low-temperature heat source such as warm water, low-pressure steam or air.
*2) Capesize is the largest class of cargo ships in the classification of sizes according to the carrying capacity.
*3) The International Maritime Organization (IMO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations established in 1958 to promote cooperation among governments concerning maritime safety, the prevention of pollution and other matters in the shipping industry.
*4) This research and development project was adopted as a project subsidized by the next-generation marine environment-related technology development support program of Japan's Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism and also adopted as a joint research theme under ClassNK. The project was undertaken with their cooperation.

(Note) The information on this web site is presented "as is." Product availability, organization, and other content may differ from the time the information was originally posted. Changes may take place without notice.