Home > Titanium > Characteristics
 Characteristics
Characteristics
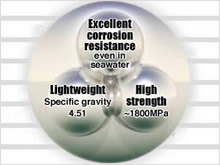
Highest Specific Strength of Existing Metallic Materials
![]()

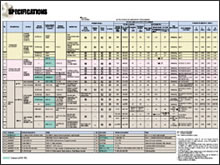
| Characteristics | Examples | Representative Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Excellent in corrosion resistance | Perfectly resistant to seawater | Heat exchangers, construction material |
| Lightweight | Lightweight equivalent to 60% of stainless steel | Airplane engines |
| High strength | Tensile strength of 275-735MPa in commercially pure titanium and of 620-1800MPa in titanium alloys |
|
| Excellent in elasticity | Modulus of longitudinal elasticity (Young's modulus) equivalent to approximately 50% of stainless steel |
Golf club heads, springs |
| Excellent in low temperature tenacity | Both commercially pure titanium and titanium alloys do not become brittle at extremely low temperatures. |
Liquefied oxygen tanks |
| Low thermal conductivity | Thermal conductivity equivalent to approximately 8% of aluminum, equal to stainless steel |
Jig and tools for molten metal |
| Easy temperature rise | Heat capacity equivalent to approximately 60% of stainless steel | Pots and fry pans |
| High resistance to thermal shrink | Thermal expansion rates equivalent to approximately 50% of stainless steel | Construction material, semiconductormanufacturing equipments |
| High electric resistance | Electric resistance 30 times as high as copper, excellent in resistance welding performance |
Seam welding of roof members, etc. |
| Extremely low magnetism | Magnetic permeability 1.00005 | Electronic devices (Stepper, etc.) |
| Superconductivity | Manifestation in Ti-Nb base alloy | Super induction motors, magnetic float trains |
| Excellent in biocompatibility | Less ions fluent in body. Less toxicity | Artificial joints, tooth roots, and cardiac valves |
| Gentle to skin | Excellent control effects against metal allergies | Watches, neck laces |
| Hydrogen occlusion | Manifestation in Ti-Fe base alloy | Hydrogen gas feeders |
| Short radioactive half value period | Half life shorter than iron, nickel, and chrome | Radioactive wastes disposing and storing vessels |
| Incombustible | Authorized as incombustible material (Authorized No. NM-8596) | Construction material |
| High class image | Used as the housings for high class cameras and personal computers | Housings of high class cameras and personal computers |
| Excellent in design properties | Coloring by cathode oxidizing treatment available | Monuments |
PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
![]()
| Commercially pure titanium |
Titanium alloy Ti-6AI-4V |
Iron | SUS 304 | Super stainless steel | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Austenitic | Ferrite | |||||
| Atomic number | 22 | - | 26 | - | - | - |
| Atomic weight | 47.9 | - | 55.8 | - | - | - |
| Crystalline structure | HCP< 885°C <BCC |
HCP< approx.990°C <BCC |
BCC< 830°C <FCC |
FCC | FCC | BCC |
| Specific gravity | 4.51 | 4.42 | 7.9 | 8.0 | 8.0 | 8.0 |
| Melting point(°C) | 1668 | 1540- 1650 |
1530 | 1400- 1427 |
1320- 1400 |
1400 |
| Young's modulus GPa | 106 | 113 | 192 | 199 | 204 | 215 |
| Poisson's ratio | 0.34 | 0.30-0.33 | 0.31 | 0.29 | - | - |
| Electric resistance (μ Ω-cm, 20°C) |
47-55 | 171 | 9.7 | 72 | 90 | 72 |
| Electric conductivity to Cu | 3.1 | 1.1 | 18.0 | 2.4 | 1.9 | 2.4 |
| Thermal conductivity (W/m°C) |
17 | 7.5 | 62 | 16 | 13 | 17 |
| Thermal expansioncoefficient (X10-6/°C)[0˜100°C] |
8.4 | 8.8 | 12 | 17 | 16 | 16 |
| Specific heat(J/kg-K) | 520 | 520 | 460 | 500 | 500 | 450 |
| Heat capacity (J/m3-K) |
2.4 X 106 |
2.3 X 106 |
3.6 X 106 |
4.0 X 106 |
4.0 X 106 |
3.6 X 106 |
| Aluminum | Aluminum alloy 7075 |
Magnesium alloy AZ31 |
Hastelloy C |
Copper | Zirconium | Glass | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Atomic number | 13 | - | - | - | 29 | 40 | - |
| Atomic weight | 27.0 | - | - | - | 63.5 | 91.2 | - |
| Crystalline structure | FCC | FCC | HCP | FCC | FCC | HCP< 863°C <BCC |
amor phous |
| Specific gravity | 2.7 | 2.8 | 1.8 | 8.9 | 8.9 | 6.5 | 2.4 |
| Melting point(°C) | 660 | 476-638 | 838-905 | 1305 | 1083 | 1852 | 800 |
| Young's modulus GPa | 69 | 71 | 45 | 205 | 117 | 89 | 98 |
| Poisson's ratio | 0.33 | 0.33 | 0.35 | - | 0.34 | 0.33 | 0.24 |
| Electric resistance (μ Ω-cm, 20°C) |
2.7 | 5.8 | 9.3 | 130 | 1.7 | 40-54 | - |
| Electric conductivity to Cu | 64.0 | 30.0 | 18.5 | 1.3 | 100 | 3.1 | - |
| Thermal conductivity (W/m°C) |
203 | 120 | 96 | 12 | 381 | 17 | 1 |
| Thermal expansioncoefficient (X10-6/°C)[0˜100°C] |
23 | 23 | 26 | 12 | 17 | 6 | 9 |
| Specific heat(J/kg-K) | 880 | 960 | 960 | 1050 | 390 | 290 | 1050 |
| Heat capacity (J/m3-K) |
2.4 X 106 |
2.7 X 106 |
1.9 X 106 |
3.5 X 106 |
3.5 X 106 |
1.9 X 106 |
2.5 X 106 |
The values listed above are the representative values. Where the values other than those of titanium are used for design, etc., it is recommended to inquire about the details to the manufacturer of each material or otherwise to verify them in the relevant expertise books.
TITANIUM CLASSIFICATION
![]()
| Classification | Representative examples | Features | Representative applications |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Name | Tensile strength (representative value) MPa |
||||||
| Commercially pure titanium | JIS | Class-1 | 320 |
Excellent in corrosion resistance and formability |
|||
| Class-2 | 415 | ||||||
| Class-3 | 545 | ||||||
| Class-4 | 650 | ||||||
| Titanium alloy |
Corrosion resistant alloy (Small amount of the platinum group element is added) |
Ti-0.15Pd | Same level as commercially pure titanium |
Corrosion resistance higher than commercially pure titanium |
|||
| α type | Ti-5Al-2.5Sn | 860 | Excellent in heat resistance and low temperature properties |
Liquefied fuel tanks for rocket applications (ELI*1Grade used) |
|||
| α-β type | Ti-6Al-4V | 960 | High strength, high ductility | ||||
| 1170 (STA*3) |
|||||||
| β type | Ti-15V-3Cr-3Sn-3Al | 830 (ST*2) |
Cold processing available |
Low Young's modulus |
|||
| 1400 (STA*3) |
Extra high strength obtainable |
||||||
| *1 ELI : Extra low interstitial *2 ST : Solution treatment *3 STA : Solution treatment and aging |
Tensile strength: Strength value subject to annealed condition, unless otherwise specially indicated |