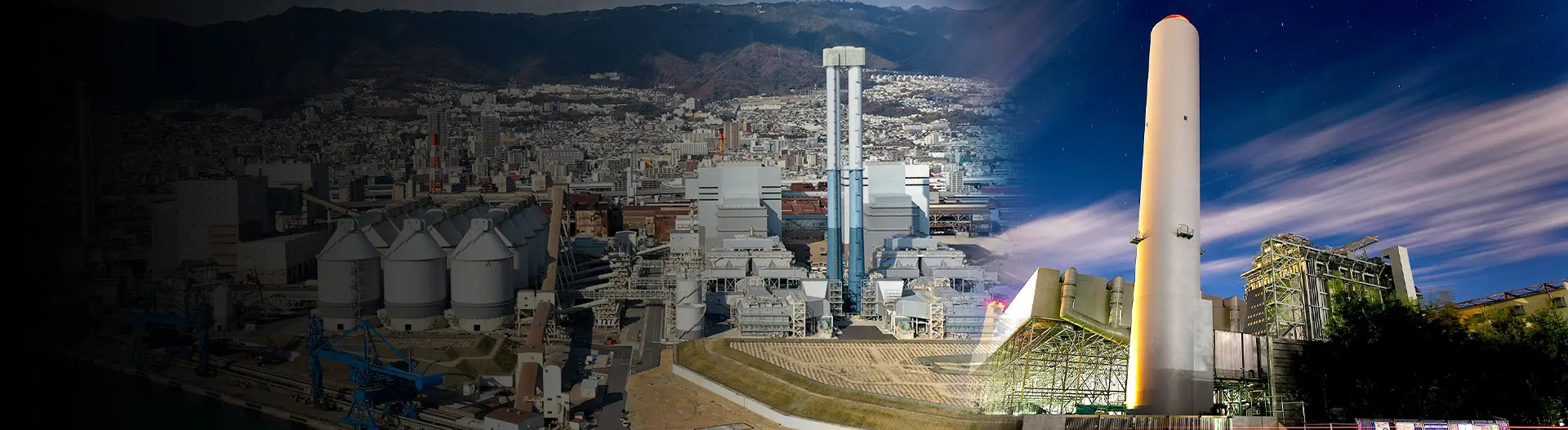


Electric Power
We contribute to the stable supply of electricity by operating power plants equipped with cutting-edge environmental technology, while also ensuring a stable profit base.
Our Electric Power Business

Following the amendment to the Electricity Business Act in 1995, which allowed non-electric power companies to sell electricity to electric power companies, our Group built a power plant in Kobe to lanch a new business, utilizing the existing infrastructure at the former Kobe Works (current Kobe Wire Rod & Bar Plant) and the know-how gained from in-house power generation in our ironmaking operations. Our wholesale power supply business began in fiscal 2002.
We currently own four coal-fired power generation facilities in Kobe, Hyogo Prefecture (Kobe Power Plant No. 1 to No. 4 units) and two gas-fired power generation facilities in Moka, Tochigi Prefecture (Moka Power Plant No. 1 and No. 2 units).
| Kobe Power Plant | Moka Power Plant | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. 1 unit | No. 2 unit | No. 3 unit | No. 4 unit | No. 1 unit | No. 2 unit | |
| Power generation capacity | 700 MW | 700 MW | 650 MW | 650 MW | 624 MW | 624 MW |
| Fuel | Coal | Coal | City gas | |||
| Power generation method | Pulverized coal-fired, supercritical (SC) pressure power generation | Pulverized coal-fired, ultra-supercritical (USC) pressure power generation | Gas turbine combined cycle (GTCC) | |||
| Operating company | Kobelco Power Kobe, Inc. | Kobelco Power Kobe No. 2, Inc. | Kobelco Power Moka, Inc. | |||
| Start of commercial operation | Apr. 2002 | Apr. 2004 | Feb. 2022 | Feb. 2023 | Oct. 2019 | Mar. 2020 |
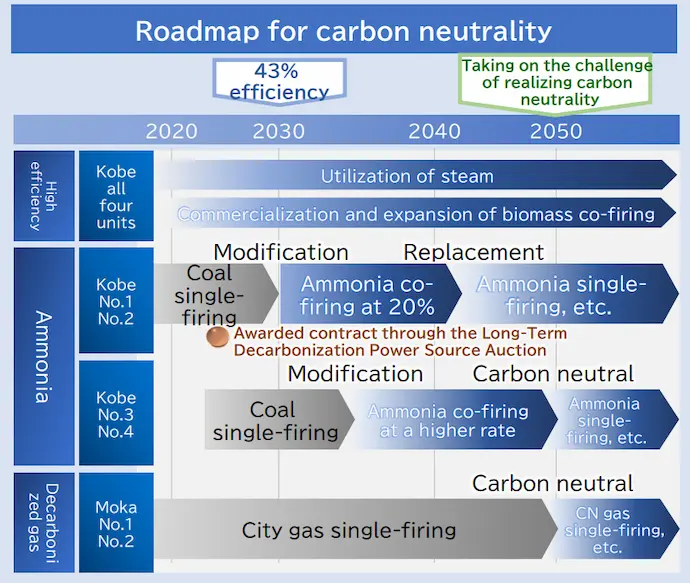
Roadmap to Carbon Neutrality
We have developed a roadmap for achieving carbon neutrality by 2050.
At the Kobe Power Plant, we are strengthening our efforts to reduce CO2 emissions by promoting the co-firing of ammonia and biomass fuels (sewage sludge, food residue), while also effectively utilizing waste heat from the power plant to supply steam to a nearby sake brewery. Through this, we strive to establish the world's most advanced urban coal-fired power plant. In ammonia co-firing, we work to increase the co-firing ratio and eventually aim to achieve single-fuel firing.
At the Moka Power Plant, we are considering maximizing the use of carbon-neutral city gas while ensuring stable low-CO2 power generation with a highly efficient GTCC system.
Roadmap for Carbon Neutrality in the Electric Power Business
History of the Electric Power Business
| 1959 | Decides to generate electricity in-house rather than using a thermal power plant jointly operated with electric power companies for the startup of the first blast furnace at Kobe Works (the current Kobe Wire Rod & Bar Plant). |
|---|---|
| 1990s | Starts "deemed wholesale electricity bussiness" at Kakogawa Works |
| 1995 | Great Hanshin-Awaji Earthquake Amendment to the Electricity Business Act; allowing non-electric power companies to supply electricity |
| 1996-1997 | Receives a thermal power supply contract from The Kansai Electric Power Co. Inc. through bidding for a tender |
| 2002 | Starts Kobe Power Plant No. 1 unit operations |
| 2004 | Starts Kobe Power Plant No. 2 unit operations |
| 2011 | Great East Japan Earthquake—Power crisis caused by the shutdown of a damaged nuclear power plant |
| 2013 | Announces the consolidation of upstream operations at Kobe Works and Kakogawa Works |
| 2014 | Places a bid for a thermal power supply tender by The Kansai Electric Power Co. Inc. Enters into a power supply contract with Tokyo Gas Co., Ltd. based on the basic agreement to supply the electricity generated by Kobe Steel in Moka to Tokyo Gas |
| 2015 | Enters into a thermal power supply contract with The Kansai Electric Power Co. Inc. through the tender process |
| 2017 | Suspends upstream operations at Kobe Works |
| 2019 | Starts Moka Power Plant No. 1 unit operations |
| 2020 | Starts Moka Power Plant No. 2 unit operations |
| 2022 | Starts Kobe Power Plant No. 3 unit operations |
| 2023 | Starts Kobe Power Plant No. 4 unit operations |
