In order to make effective use of limited resources, the Kobe Steel Group implements measures to control waste at its offices and plants.
We add value to byproducts created during manufacturing processes, develop and introduce new applications for materials, and actively pursue recycling.
Additionally, we also promote recycling and reuse during shipping through changes to packaging methods. We’re also working to reduce paper consumption at offices by proactively digitizing meeting materials and introducing IT solutions throughout the Group.
In fiscal 2016, a total of 5.25 million tons of byproduct materials were created by the Kobe Steel Group, including overseas Group companies, with approximately 92.9 percent coming from the Iron & Steel Business. At the steelworks, we strive to recycle and add value to items such as slag (a secondary material produced during iron and steelmaking) and dust.
In fiscal 2016, due to a relining of a blast furnace, a temporary cause in the Iron & Steel Business, the overall recycling ratio for Kobe Steel was 95.6 percent, while the overall ratio for the Kobe Steel Group (including overseas Group companies) was 95.8 percent.
The Kobe Steel Group follows a fundamental policy of reducing the volume of waste generated, through methods such as improvements to yield rates and reduction of auxiliary materials. These policies are helping us to reach new targets for fiscal 2020 based on voluntary action plans adopted in each industry (i.e. target numbers for waste consigned to landfill and recycling).
Throughout the Kobe Steel Group, including overseas companies, Kobe Steel consigned 220,000 tons of waste to landfills. We plan to continue reducing this number by controlling the amount of waste generated, increasing recycling, developing new recycling technologies, adding value to byproducts, and other such measures.
Byproducts by Business Unit (Includes Japanese and Overseas Group Companies)
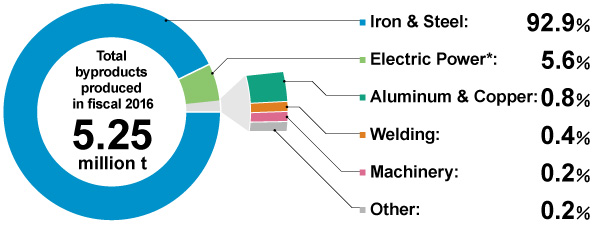
* The Electric Power Business was newly established in fiscal 2016 through merger of the Iron & Steel Business' wholesale power supply (IPP) operations with new Head Office power supply projects.
Byproducts, Amount Recycled and Recycling Ratio (Kobe Steel)
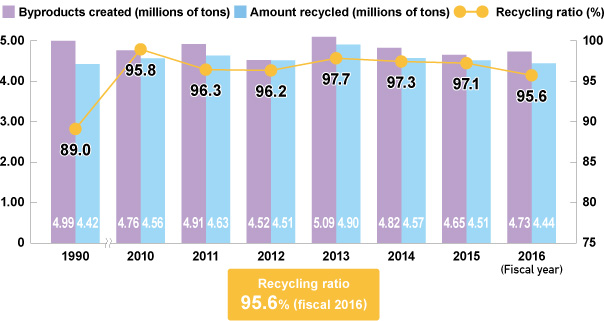
* Recycling ratio = Amount recycled/total amount of byproducts

Slag materials being used in construction
(off the Suma coast)

Kobe Steel continues to develop new technologies for the recycling of dust, as well as reduce and develop new uses for steel slag. As a result, in fiscal 2016 Kakogawa Works, Kobe Works and Takasago Works limited waste consigned to landfills to approximately 180,000 tons.
In fiscal 2016, 2.33 million tons of blast furnace slag and 950,000 tons of steel slag were produced at Kakogawa Works and Kobe Works. These works pursue appropriate operation and management, in line with the “Guidelines for Management of Iron and Steel Slag Products” established by the Nippon Slag Association.
As part of research into development of new uses for recycled slag, demonstration tests were held at Iwaya Port (Awaji Island, Hyogo Prefecture). The tests established that slag can possess exceptional environmental value and be used to promote the growth of seaweed beds. In March 2016 1,000 tons of slag were used for the first time as submerged breakwater materials for construction in the waters of Kobe City in Hyogo Prefecture (for the Suma District breakwater construction project). Moving forward, Kobe Steel will continue to work to improve ocean environments, promoting use of steel slag as an alternative to natural stone during ocean construction.
The Welding Business established resource recycling action plans and pursues a variety of measures at each of its locations. The know-how behind such measures is shared throughout the Business via regular meetings.
At locations in Japan we sort waste flux for recycling as roadbed, cement and other such materials. We are also expanding reuse of product packaging materials, in place in locations in Japan, to overseas locations, in an effort to reduce waste.
In the Aluminum & Copper Business, we not only engage in initiatives to limit waste at business locations, but also collaborate with other business units in efforts to improve resource recycling rates.
Aluminum ash produced during welding at the Moka Plant is utilized during hot metal desulfurization at the Kakogawa Works. Additionally, the recycling ratio at the Moka Plant reached an all-time high in fiscal 2016 of 96.5 percent.
At overseas Group companies, we are working to improve yield by cooperating with domestic locations to reduce occurrence of material scrap.
Moka Plant Recycling Ratio
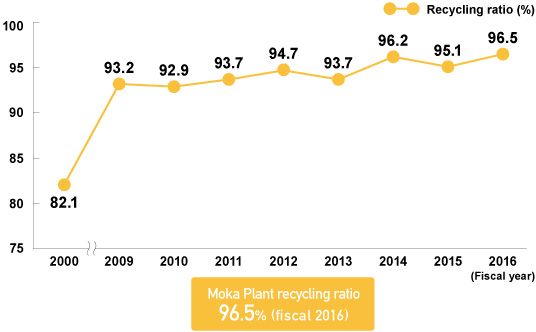
* Recycling ratio = (intermediate processing amount+recycled amount)/total amount of waste
In the Machinery Business, a high resource recycling ratio is maintained through the entrenchment and continuation of previously implemented measures.
The Harima Plant, which manufactures standard compressors, reduces waste through adoption of reusable shipping cartons (made with stronger packing materials for repeated use) when transporting goods from local and overseas suppliers. Additionally, used paper, which was previously incinerated, is now recycled.
The Takasago Works, which manufactures nonstandard compressors and industrial machinery, strives to extend the life of cutting tools used during processing by resharpening them, as well as to filter and recycle hydraulic fluid used during trial runs.

Coal ash silo

At the Kobe Power Plant of Kobelco Power Kobe, Inc., which operates under our wholesale power supply business, coal ash produced after burning coal for fuel and calcium sulphate emitted by flue gas desulfurization equipment are held in storage silos and entirely recycled as raw materials for cement.