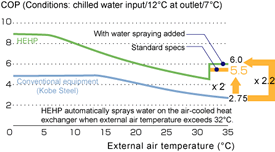
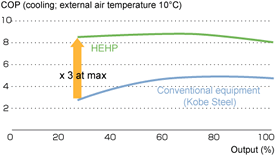
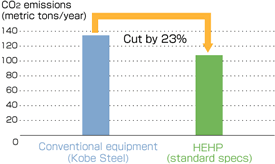
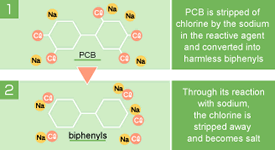
Home > About Us > Corporate Social Responsibility > Sustainability Report > Sustainability Report 2007 > 2.Products, Technologies and Services to Benefit the Environment
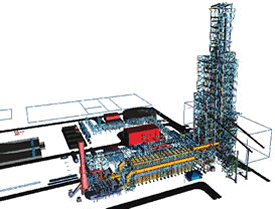
 Groundbreaking ceremony for large-scale demonstration plant in Kalimantan, Indonesia)
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||