Home > About Us > Sustainability Management > Sustainability Report > Sustainability Report 2011 > Proper Control of Chemical Substances
 Proper Control of Chemical Substances
Proper Control of Chemical Substances
| Striving to reduce hazardous chemical substances by promoting control and replacement in line with domestic and overseas standards |
The Kobe Steel Group has imposed tight controls on chemical substances, reducing the quantities of hazardous materials used, and substituting safer alternatives.
Thorough Control of Chemical Substances
Having set out the Kobe Steel Group Policy on Controlling Hazardous Substances, we make every effort to effectively control chemical substances. For example, Management Sheets for Designated Chemical Substances are used by all group companies to clearly specify usage and control methods for each substance. Sheets are used to calculate volumes transferred or released for notification in accordance with the PRTR Act* and also as part of activities aimed at reducing consumption and emissions of chemical substances.
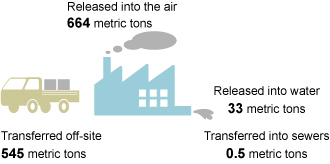
Notifications submitted in accordance with the PRTR Act in fiscal 2010 indicate that the Kobe Steel Group handled 50 designated substances, released approximately 697 metric tons and transferred approximately 545 metric tons. A full list of substances for which notification is scheduled to be submitted by the Kobe Steel Group is available on this website.
| * | PRTR Act: Pollutant Release and Transfer Register: Legislation that requires notification of the releases of designated chemical substances into the environment and promotes improved controls. |
| Combined total for chemical substances released into the air and water | |
| Combined total for chemical substances transferred off-site or into the sewers |
Chemical Substances Released and Transferred by the Kobe Steel Group
Meeting Regulations on Chemical Substances
Regulations on chemical substances are becoming increasingly strict, not only in Japan but all over the world. In Japan, new requirements were introduced in fiscal 2010 as a result of revisions to the Chemical Substance Control Act* and the PRTR Act.
As new chemical regulations have also been introduced in areas such as Taiwan and China, we are working to share information and exchange opinions between relevant departments within the Kobe Steel Group in order to ensure adequate compliance with all relevant legislation.
* Chemical Substance Control Act: Act on the Evaluation of Chemical Substances and the Regulation of their ManufactureControlling Waste Electrical Equipment Containing PCBs
In accordance with government regulations on the proper handling of wastes containing polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs), equipment such as transformers and condensers that contain PCBs are placed in special storage facilities when no longer used, with notification made to government authorities.
We began outsourcing the disposal of PCBs in fiscal 2008 and continued to do so at each of our works (Kakogawa Works, Kobe Works and Takasago Works) during fiscal 2010.
Efforts to Reduce Chemical Emissions
|


