Home > About Us > Sustainability Management > Sustainability Report > Sustainability Report 2013 > Measures Against Global Warming
 Measures Against Global Warming
Measures Against Global Warming
In response to global warming, The Kobe Steel Group promotes rationalization and R&D geared toward reducing energy consumption throughout its operations, while reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
Energy Conservation during Manufacturing Processes
![]()
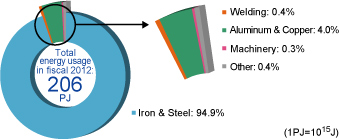
In fiscal 2012, the Kobe Steel Group used 206PJ of energy (equivalent to 5.22 million kl of crude oil).
Of that total, approximately 95% was used in the Iron & Steel Business, and approximately 4% in Aluminum & Copper.
Kobe Steel continuously strives to reduce energy consumption through such methods as improvements to productivity and fuel management, the introduction of highly efficient equipment, and the recovery of waste heat.
Energy Usage by Business Unit
Iron & Steel Business
![]()
-
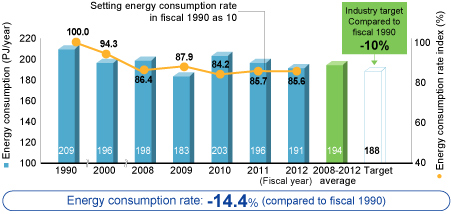
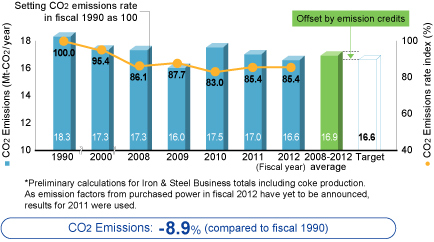
In fiscal 2012 energy use in the Iron & Steel Business unit was reduced by 2.4% year-on-year while CO2 emissions were reduced by 2.3%, in part due to a decrease in production amounts. Compared to the base year (1990), the energy consumption rate per ton of crude steel improved by 14.4%, while the CO2 emissions rate per ton of crude steel improved by 14.6%.
Aiming for even greater efficiency of its private power station, the Kakogawa Works is in the process of constructing a second high efficiency gas turbine. The first turbine was put into operation in 2011.
At all sites, meticulous efforts are being carried out to increase the efficiency of pumps and fans, improve the operation of heating furnaces, and otherwise reduce loss.
In the future, we will continue to implement energy conservation measures so as to reduce the environmental burden.
-

Private power station under
construction at Kakogawa
Works
Energy Consumption/Energy Consumption Rate Index (Preliminary Calculations)
CO2 Emissions/ CO2 Emissions Rate Index (Preliminary Calculations)
Welding Business
![]()
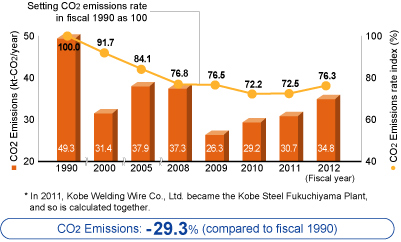
Through efforts to reduce loss, such as improvements to productivity and optimization of equipment, the Welding Business aims to reduce CO2 emissions. In fiscal 2012, through measures such as changes to fuel and optimization of lighting, the Ibaraki Plant reduced CO2 emissions by 29.3% in comparison to 1990, and the CO2 emission rate per ton of product by 23.7%.
CO2 Emissions/ CO2 Emissions Rate Index (Preliminary Calculations)
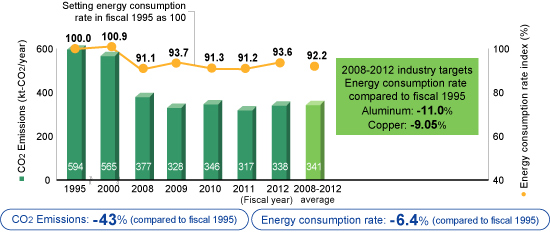
Aluminum & Copper Business
![]()
The Aluminum & Copper Business has been switching from oil-based fuels to natural gas, as well as pursuing equipment intensification and efficiency. In fiscal 2012 the fuel was changed for melting furnaces (Moka Plant) and inverters were added to fans, reducing CO2 emissions by 43% compared to the base year (fiscal 1995) and reducing the emissions rate by 6.4%.
Additionally the Japan Aluminium Association industry targets for fiscal 2008-2012 are expected to be met.
CO2 Emissions/Energy Consumption Rate Index (Preliminary Calculations)
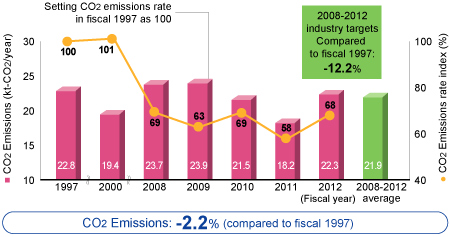
Machinery Business
![]()
As demand for products such as energy-saving compressors, heat pumps and heavy-wall pressure vessels for the oil-refining sector increases, the Machinery Business is also striving to increase energy efficiency through optimization of equipment and improvements to productivity. In fiscal 2012, CO2 emissions were improved by 2.2% compared to the base year (fiscal 1997), and the CO2 emission rate was improved by 32%.
Additionally the Japan Society of Industrial Machinery Manufacturers industry targets for fiscal 2008-2012 are expected to be met.
CO2 Emissions/CO2 Emissions Rate Index (Preliminary Calculations)
Energy Conservation in Distribution
![]()
-
From raw materials to product shipment, the Kobe Steel Group aims to reduce energy consumption by using optimal distribution channels. Shipping efficiency is improved through expansion of modal shifts from truck to rail and ocean freight, greater loading efficiency, and larger rail cars. Additionally, the use of return cargo reduces wasted transportation of empty freighters.
We also work to reduce fuel consumption through the use of state-of-the-art cargo ships to transport steel products and lighter freight cars.
-
After delivering products, Kobe Steel endeavors
to acquire return cargo so as to avoid empty
freighters on return trips.
Group Company Initiatives
![]()
Individual Kobe Steel Group companies also strive to reduce energy during manufacturing processes and distribution. In addition to the initiatives mentioned below, Group companies also implement measures to turn off lights, regulate air conditioning, and otherwise conserve energy,
Examples of Initiatives
| Company name | Location | Example of initiatives |
|---|---|---|
| Shinko Wire Company, Ltd. | Amagasaki, Hyogo Prefecture | Inverters added to equipment, high-efficiency transformers installed, switched to efficient lighting |
| Shinko Fab Tech, Ltd. | Shimonoseki, Yamaguchi Prefecture | Improvements to melting furnace regenerative burner, upgrade of refractory at furnace walls |
| Kobe Welding of Qingdao Co., Ltd. | Qingdao, Shandong Province, China | Installation of highly efficient air conditioning and lighting |
TOPICS
Environment Minister's Award for Global Warming Prevention Activity, Implementation of Countermeasures Category, Kakogawa Works
Eco-Commuting Program Reduces CO2 Emissions by Approximately 7,500 Tons over Three Years

Former Deputy General Manager
Aritsune Iwasaki (right)
receiving prize from then current
Minister of the Environment Hiroyuki
Nagahama

Commuting after implementation
of the Eco-Commuter Program
The Kakogawa Works' Eco-Commuting Program, which earned the Environment Minister's Award for Global Warming Prevention Activity, was instituted in 2008. The program, which urges the work's approximately 10,000 employees to commute by public transportation rather than private cars, helps to reduce CO2 created by the use of private cars.
In order to make the program a success it was necessary to improve alternate means of transportation, such as increasing the number of buses, making changes to schedules, and adding additional routes. We also created separate lanes on company grounds for those commuting by bicycle or foot so as to ensure their safety. Additionally, from the program's inception, we introduced hybrid buses so as to further reduce environmental impact.
Thanks to these efforts, the use of private cars by employees commuting to the works, which exceeded 8,000 cars per day before implementation of the program, was, as of June 2012, cut approximately in half, to 4,100 cars.
The Minister's Award was given in recognition of the accompanying reduction to CO2 emissions, with a total reduction of approximately 7,500 tons over the period from June 2009 to March 2012. With cooperation from employees and affiliated companies, we will continue to promote the Eco-Commuting Program at Kakogawa Works.


