Manufacturing Process for Aluminum Extruded Products
Overview of the Aluminum Extrusion Process
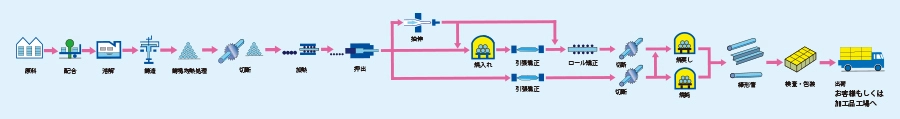
Typical Manufacturing Process

- (1) Melting and Casting
Aluminum ingots and various alloying elements are melted in a melting furnace.
In the subsequent casting process, the molten aluminumis poured into molds to form billets.

- (2) Homogenization
To eliminate micro-segregation that occurs during solidification, the billets undergo homogenization treatment—heating and holding the billet at a controlled temperature.
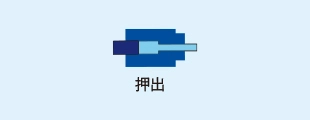
- (3) Extrusion
The billets are cut and heated, then placed into a pressure-resistant vessel called a container. Using a ram (stem), the material is pushed through a die with a hole at the end of the container. The holes in the die determine the final form of the extruded bar stock.

- (4) Heat Treatment
The extruded material is sent to the heat treatment process, where it undergoes quenching, annealing, or tempering depending on the intended application and required temper designation.
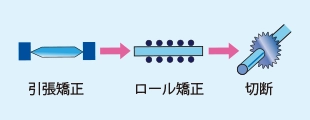
- (5) Cold Working and Straightening
After extrusion, cold working processes such as drawing or straightening (either tensile straightening or roll straightening) are applied, based on the product's intended use.
- (6) Inspection
Each product undergoes various inspection, including dimensional checks, surface inspection, and mechanical property testing (e.g., tensile strength) to confirm that it meets quality standards.
Contact Us
You can reach us by clicking the inquiry button.